Global wireless CapEx is on the rise, as operators deploy LTE and HetNet (Heterogeneous Network) infrastructure, amid growing demands for high-speed mobile broadband connectivity. By eliminating reliance on expensive proprietary hardware platforms, NFV (Network Functions Visualization) and SDN (Software Defined Networking) promise to reduce the CapEx burden on wireless carriers. In addition, both technologies can significantly slash OpEx due to a reduction in physical space, labor and power consumption.
Driven by the promise of TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) reduction, operators are aggressively jumping on the NFV and SDN bandwagon, targeting deployments across a multitude of areas. By the end of 2020, SNS Research estimates that NFV and SDN investments on operator networks will account for nearly $21 Billion. These investments will primarily focus on mobile core/EPC, policy/IMS services, RAN (Radio Access Networks), OSS/BSS, data center, backhaul and CPE/home environment.
Software defined networking (SDN), network function virtualization (NFV), self-organizing network (SON), orchestration and cloud-based solutions are some the technologies that must for the foundation of this next generation technology architecture.
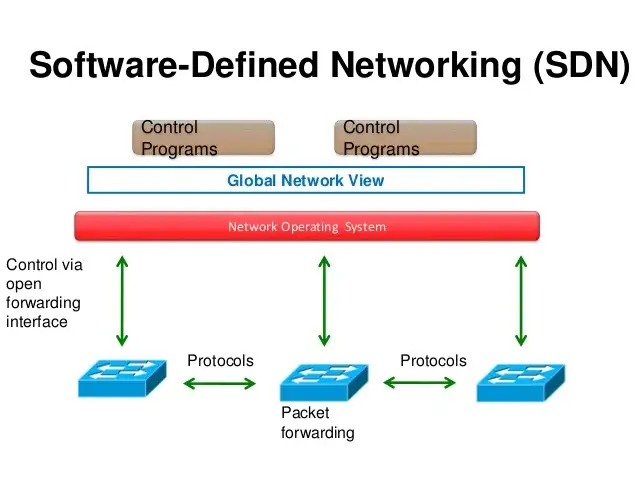
Software Defined Networking (SDN)
A much talked about technology in recent times, SDN is now apparently becoming a requisite for the enterprise world.SDN assumes the segregation of the Network Functions (NFs) control and data planes, being NF data forwarding process fully commanded by control-level applications through programmatic means (high-level APIs) abstracting the specific network details.SDN stimulate the centralization of control functions in SDN Control Applications, creating a new paradigm for data plane control. Due to the holistic network view, this new paradigm enables the enforcement of control decisions considering the end-2-end state of the controlled network infrastructure. This approach will bring additional flexibility and agility in network control when compared to traditional networks. Centralized SDN Control Applications also act as a central point for the data plane functions configuration, exposing API’s for northbound clients such as the operational management processes, contributing in this sense to facilitate end-2-end service management over the controlled domains.
Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
NFV can potentially take any network function normally residing in purpose-built hardware and abstract it from that hardware. Once abstracted, the function can be managed as a software module that is deployed on a standard computing platform. It can also be moved to or replicated on another hardware or computing platform.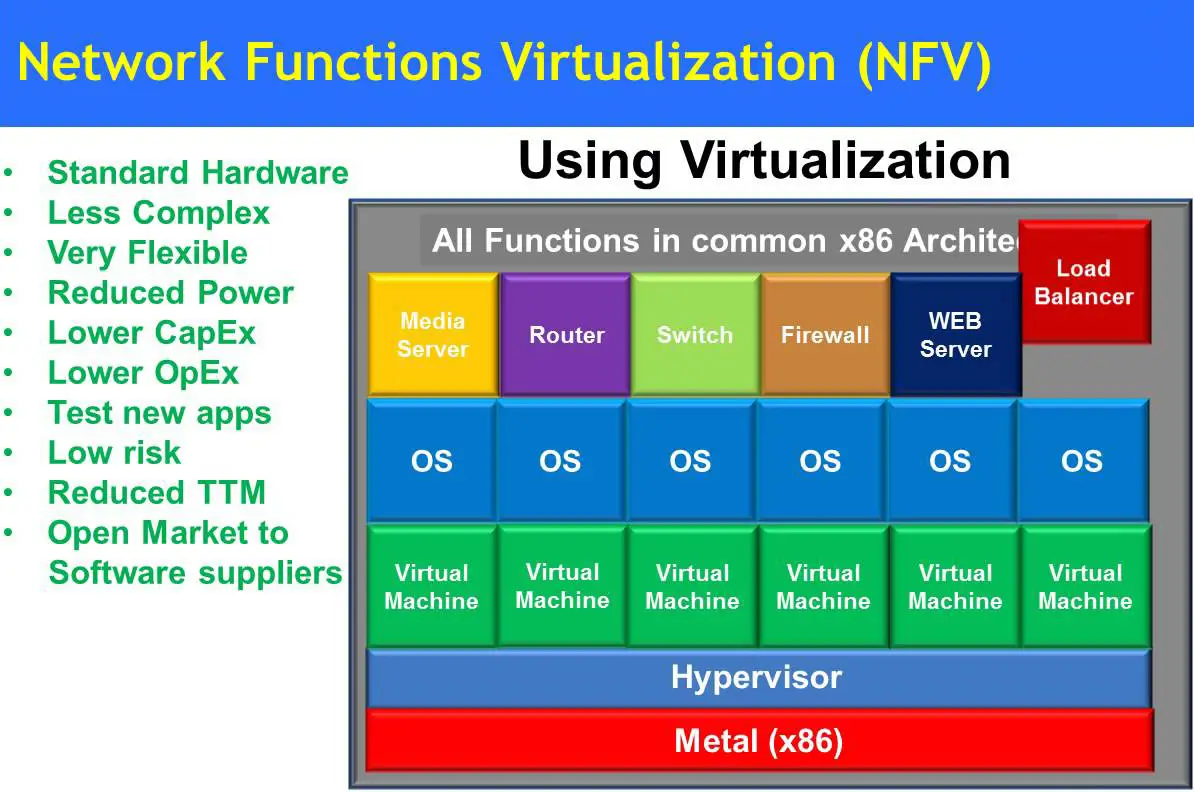
NFV helps you move away from multiple isolated networks, custom-built equipment, and complex operations. Instead, you work with an open ecosystem and an orchestrated set of virtualized network functions (VNFs).NFV aims to transform network architectures by implementing network functions in software that can run on common purpose virtualized infrastructure built on top of industry standard hardware. Benefiting from IT Cloud Management evolution, especially the evolution in VIM (Virtual Infrastructure Management) platforms (e.g., OpenStack), the evolution towards an NFV enabled service architecture will lead to the creation of a new service environment, built over a mesh of micro data centres, the new service platforms.
These platforms, including advanced virtual infrastructure management platforms, will provide enhanced agility for new services creation and management, being also a contributor for costs reduction due to use of common purpose hardware.
At present time, the creation of a new service requires the setup of an engineering project to coordinate and govern the configuration of several distinct network elements (appliances) and the creation of specific service logic in proprietary service delivery and control platforms.
NFV SDN Advantages
NFV and SDN are not dependent on each other and can exist separately. However, the evolution to a virtualized network architecture (NFV) and the implementation of new service scenarios make SDN an indispensable partner to NFV.
One of the major service enhancements typically associated with NFV is in fact leveraged on the top of the capability to dynamically and automatically create specific chains of network functions to associate to a specific user service context, a capability powered by SDN.
The new service scenarios rely on dynamic and automated virtual network functions reconfiguration, scalability, and even migration between several service provider data centres.
Major factor for service enhancement, the network functions lifecycle dynamicity requires the ability to automatically reconfigure the connectivity topology linking the network functions. SDN responds to this challenge.
The SDN/NFV Challenge
Both technologies will potentially sweep away the dozens, or even hundreds of vendor-specific, technology-specific and/or service-specific network management tools that service providers use to configure, monitor, and troubleshoot the multiplicity of physical devices at different layers of their networks.SDN and NFV promise high levels of management automation, the brutal truth is that large numbers of operational staff may no longer be needed if and when they are deployed.
The Legacy and NFV networks will co-exist for next few years, and operators need to focus on NFV, while not neglecting legacy, where their existing customer rides
Migration to new NFV network is another challenge, as this involves huge planning, testing and co-ordination with customers
Since this is new technology, CSPs are expected to invest huge resources in POC, testing, use cases and field prototype creation
The speedy orchestration of an end-to-end service which traverses a chained sequence of VNFs (Virtualized Network Functions). The OpenFlow protocol is used for orchestrating the forwarding layer in routing and switching VNFs. However, this is not uniformly supported across all VNFs. The overall network orchestration layer needs to support a multitude of protocols and APIs to automate end-to-end service provisioning in a truly dynamic environment.
One of the key benefits of a virtualized infrastructure that operators want to capitalize upon is the ability to auto-scale the network capacity on demand to adjust to the dynamic nature of traffic. In order to auto-scale a VNF up or down, a real-time monitoring capability that provides the key performance metrics in a timely fashion to the auto-scaling application is essential.
Overcoming Challenges
Clearly SDN and NFV help virtualize networks and maximize Opex/Capex. However a significant barrier to adoption and scale is legacy networks.
centralized management.
centered on sustaining profitable growth, redefining value, delivering customer experience, innovating, competing successfully.
Economies are transitioning towards the Internet of Everything, which will need networks to transform and scale rapidly.
As service providers remodel their businesses from voice-centric to data-centric, they will be able to reduce costs, improve efficiency and resource usage, while growing their business. They will also be able to create new revenue-generating service and show a superior financial performance compared to their peers in the market.
For more information about NFV, SDN and WirelessNetwork Infrastructure please Drop an email on info@oditeksolutions.com