[slider]ROBOT FRAMEWORK which is a generic test automation framework for acceptance testing and its tabular test data syntax is almost plain English and easy to understand. Its testing capabilities can be extended by test libraries implemented either with Python or Java, and users can create new higher-level keywords from existing ones using the same syntax that is used for creating test cases. Robot Framework itself is open source and most of the libraries and tools in the ecosystem are also open source.
Robot Framework comes from its user keyword feature: in addition to the keywords provided by the extension libraries, users can create new higher-level keywords from the existing ones using the same syntax that is used for creating test cases. And, of course, everything can be parametrized with variables.
Test cases are always executed within a test suite. A test suite created from a test case file has tests directly, whereas suites created from directories have child test suites which either have tests or their own child suites.
Test Cases
Test Steps:
- Launch Browse
- Search Application On Google
- Launch Application
Now let’s give structure to our above Test Case as per Robot Framework.
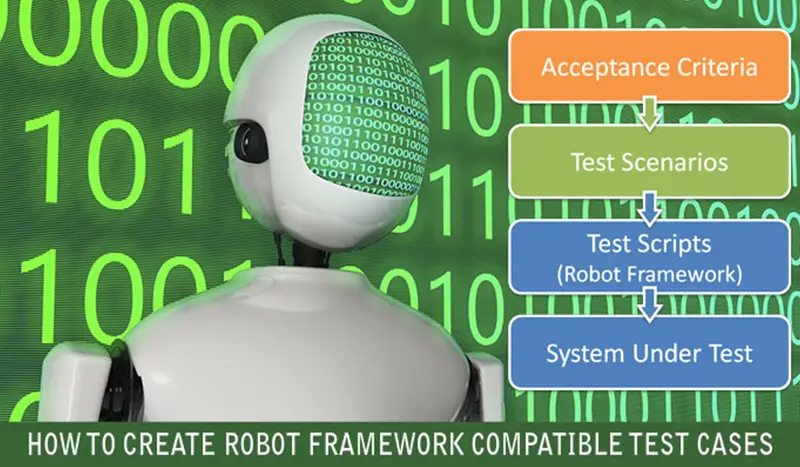
Execution flow
Everything in RF is given in the form of 4 tables which are called as “Setting”,”Variables”,”Test Cases” and “Keywords” table.
Settings: – It’s equivalent to global dependencies like if we talk about Java language it’s like import statement written before coding begins or like stdio. h header in C language. It contains the settings like a link to resources file, variable file, external libraries.
Variables: – As the name indicates it contains our declaration of variables used in the flow of RF say like URL = www.google.com
Test Cases:- It is where we are going to define our manual test case flow in the business like language thus it easily understood by nontechnical team members.
Keyword:- This is the place where real actions happen, meaning we give implementation to our above-defined test case like we say “Launch Browser” in our test cases table, then how RF know that its suppose to launch the browser. For that, we need to define the meaning of “Launch Browser” in our keywords table. Generally, we use pre-defined keywords from our external
Step by test cases
Step1:-
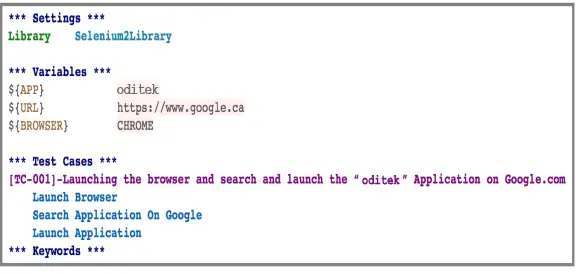
- Open the editor and create the 4 tables preceded with an asterisk (*) symbol, this is internally used by RF to distinguish the tables as anything outside these tables is redundant for RF.
- Put one space and then add the name of the table, Say *** Settings ***
Note:-
- For consistency purposes it is advisable to use 3, *** symbols in front of table name (as same would be created in RIDE).We can use * or ** or *** as all are same for RF. So don’t be confused lets have 3 *** symbols.
‘*’ at the end is not required, but again for consistency purposed we are implementing them.
Step2:-
Copy the business steps of manual test case above and add to “Test Cases” table
Note:-
- First row of the Test Cases table is used for Test Case name say for documentation.
Step3:-
Define the required variables in Variables table. Each variable is defined as ${variable name}
Step4:-
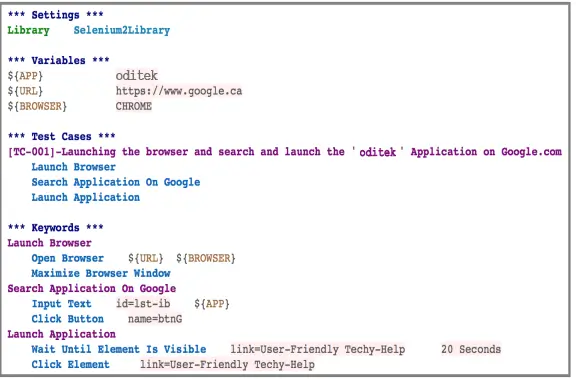
Add the required libraries in “Settings” table, we would be using Selenium2Library as we would be working with browser application thus we need the keywords defined in this library.
Step5:-
Main step to define the meaning of Keywords used in the Test Cases table. We would utilize the predefined keywords of “Selenium2Library”.
Step6:-
Save the file with .robot extension (it is same as .txt).
Note:-
- RF supports the .html format, TSV format, Plain text and restructured Text formats. In our example, we have used plain text format which is widely implemented across the industry.
- For identifying the locator properties of the object above, you can use firebug, or simply use selenium -IDE, record a script and extract properties.
Step7:-
Run the file using “pybot” interpreter.
Write the command pybot testcaseName.robot on command prompt and we are ready with results.

Note:-
Don’t worry in case the code is not running in the first go, there can be issues like spell mistakes or extra spaces, just copy the above code, save and execute it.