CUCUMBER INTRODUCTION
The Cucumber tool is based on Behavior Driven Development (BDD) framework with which one can write acceptance tests for the web application. The Cucumber in testing allows automation of functional validation in an easily readable and understandable format to BAs, developers, and testers.
Cucumber feature files serve as a good document for everyone. Many other tools support BDD frameworks like JBehave. Cucumber was initially implemented in Ruby and then was extended to the Java framework. Both tools support native JUnit.
To understand Cucumber testing better, first, understand the fundamental base and how BDD works. BDD is an amalgamation of business and technology to fulfill the objective for a particular application and validates the behaviour of the system in accordance with the desired output and thereby, assists in automated testing of any type.
THE NITTY-GRITTY OF CUCUMBER TESTING
To understand Cucumber testing, we need to know all the features of Cucumber and its usage.
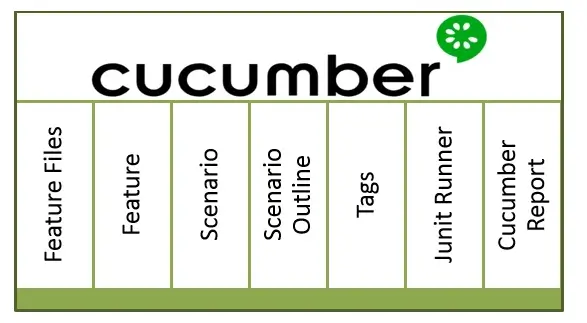
#1. Feature Files:
These files are the essential part of Cucumber which is used to write acceptance tests or automation steps. The steps are the application specification. All the feature files end with .feature extension.
#2. Feature:
This gives the information about high-level business functionality and the purpose of Application under test. Anyone who reads the first feature step should be able to understand the intent of the feature file. This part needs to be kept brief.
#3. Scenario:
It represents a particular functionality that is under test. Users should be able to understand the intent behind the scenario and what the test is all about by seeing the scenario. Each scenario should follow the format – given, when, and then. The language is known as ‘Gherkin.’
a. Given: It specifies the pre-conditions. It is a known state.
b. When: This is used when any action is to be performed.
c. Then: Any expected results or outcomes are placed here.
d. Background: Whenever any step is required to perform in each scenario then those steps need to be placed in Background.
e. And: It is used to combine two or more same type of action.
Example of Background:
Background:
Given user logged in as database administrator
And all the junk values are cleared
#4. Scenario Outline:
It is used when the same test has to be performed with a different data set. Let’s take an example – test login functionality with multiple different sets of usernames and passwords.
Feature:
To make sure login functionality works,
You should run the Cucumber testing to verify it’s working
Scenario Outline: Login functionality
Given user navigates to the login page
When the user logs in using username and password
Then login should be successful
#5. Tags:
Cucumber by default runs all scenarios in all the feature files. But there could be hundreds of feature files which does not require to run all time.
For example, Feature files related to smoke tests need to run all the time. Mention the tag as smokeless in each feature file which is related to smoke test and runs Cucumber test with @SmokeTest tag. Cucumber will run only on those feature files specific to given tags. You need to specify multiple tags in one feature file.
#6. JUnit Runner:
To run the specific feature file Cucumber uses standard JUnit Runner and specific tags in Cucumber. You can also assign multiple tags by using comma separate. Specify the type and path of the report you want to generate.
#7. Cucumber Report:
Cucumber generates its HTML format. However, better reporting can be done using a bamboo tool or Jenkins.
In this post, we have covered features of Cucumber tools and its usage in a real-time scenario. Cucumber for testing is the most preferred tool for many projects as it is readable, easy to understand, and contains business functionality.