RFID technology is significantly impacting modern business and industrial operations by enhancing tracking and automation. Its capacity to streamline processes and improve efficiency is transforming inventory management, supply chain logistics, and asset tracking.
Understanding Radio Frequency Identification
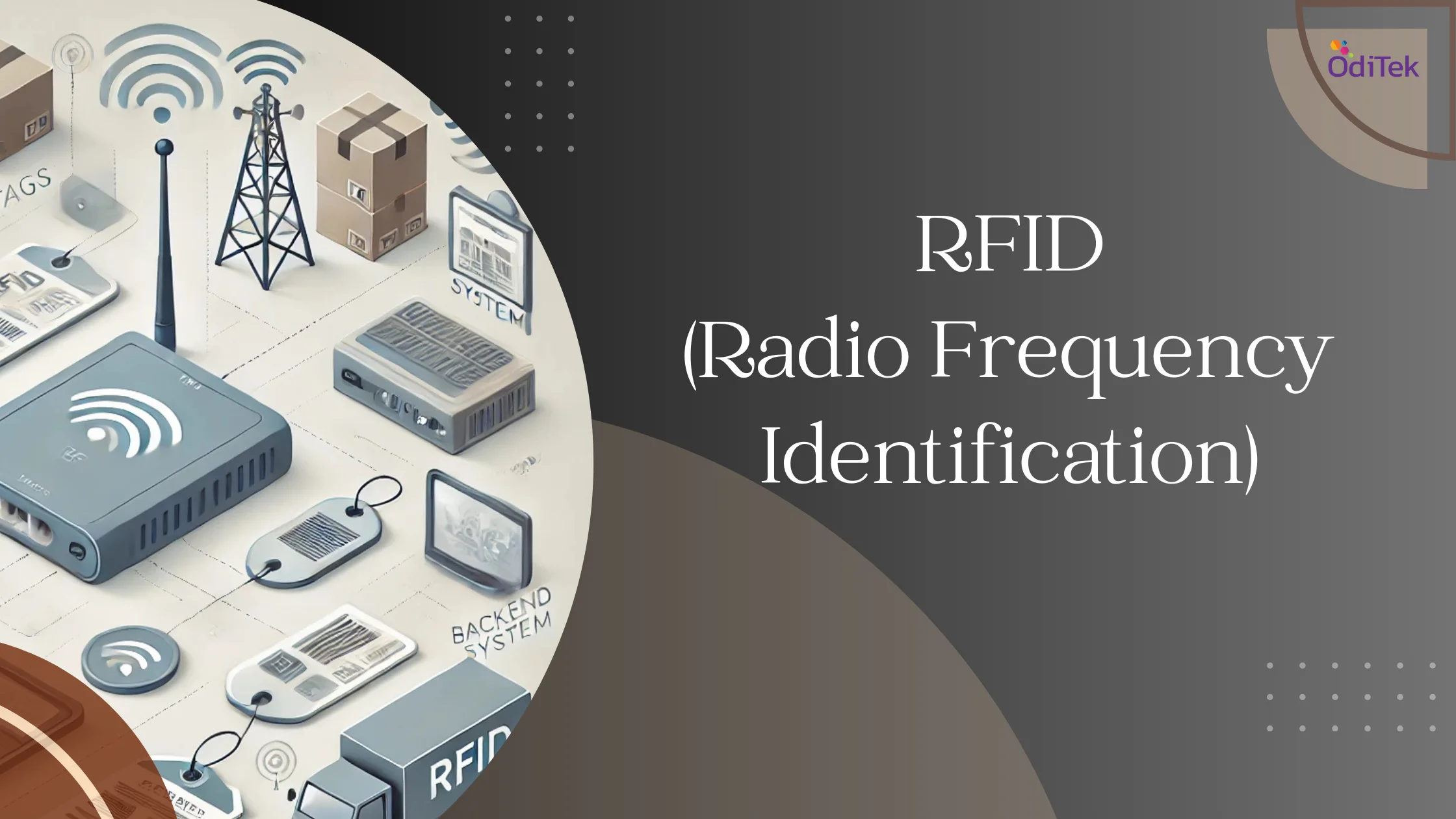
RFID is a wireless technology that utilizes electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags contain electronically stored information that can be read by an RFID reader. Unlike traditional barcode systems, RFID does not require a direct line of sight, making it a more efficient and scalable solution for tracking applications.
How Radio Frequency Identification Tracking Works
Radio Frequency Identification Tracking operates through three main components:
1. RFID Tags
Embedded with a microchip and antenna, RFID tags store crucial data that can be read wirelessly. These tags come in different forms, including passive, active, and semi-passive tags. Passive RFID tags rely on the energy from the reader’s signal to transmit data, whereas active RFID tags have an internal battery to send signals over a longer range. Semi-passive tags combine features of both, using a battery for internal operations while relying on the reader for communication.
2. RFID Readers
These devices capture data from RFID tags via radio waves and send it to a processing system. Readers can be fixed or handheld, depending on the application. Fixed readers are installed at strategic locations like entry points or conveyor belts to track movement, while handheld readers allow mobile scanning in warehouses or retail stores. Advanced RFID readers are integrated with Wi-Fi and cloud connectivity for real-time data access.
3. Backend Software
The collected data is analyzed and utilized for tracking and management. The backend system processes the data to provide insights into inventory levels, asset locations, and operational trends. Cloud-based RFID solutions enable businesses to monitor and manage their assets remotely, improving decision-making and operational efficiency.
The Role of a Radio Frequency Identification Sensor
An RFID sensor enhances the tracking system by detecting RFID signals and facilitating precise data capture. These sensors are crucial in environments where accuracy and real-time tracking are essential, such as healthcare, retail, logistics, and warehousing. RFID sensors help in:
• Monitoring inventory levels with automated stock updates.
• Enhancing security by preventing unauthorized access.
• Optimizing asset utilization through real-time tracking.
Applications of RFID Technology
1. Inventory Management
Businesses use RFID to track stock levels, reduce theft, and improve supply chain efficiency. By integrating RFID with warehouse management systems, companies can automate stock replenishment, reduce human errors, and enhance visibility across multiple locations. RFID also enables real-time tracking of high-value inventory, preventing losses due to theft or misplacement.
2. Healthcare
RFID is used for patient tracking, medication management, and equipment monitoring. Hospitals use RFID wristbands for patients to ensure accurate identification and improve safety. RFID-enabled cabinets track medication usage, reducing errors and ensuring compliance with medical regulations. Additionally, RFID helps locate medical equipment like wheelchairs, IV pumps, and defibrillators, enhancing operational efficiency.
3. Retail
Stores implement RFID to enhance checkout speed, reduce shrinkage, and improve customer experiences. RFID-enabled self-checkout systems eliminate the need for scanning barcodes, speeding up transactions. Retailers use RFID for loss prevention by tracking inventory movement in real time, helping prevent theft. Moreover, RFID improves customer experience by enabling smart fitting rooms where customers can receive product recommendations based on RFID-tagged apparel.
4. Transportation & Logistics
RFID streamlines fleet management and enhances shipment tracking. Logistics companies use RFID tags on shipping containers and pallets to monitor shipments in transit. RFID helps reduce delays by providing real-time location updates and automating customs clearance processes. In public transportation, RFID cards allow seamless ticketing systems, reducing wait times for passengers and improving operational efficiency.
Using a Radio Frequency Detector App
A Radio Frequency Detector App enables users to detect and analyze RFID signals using smartphones or dedicated handheld devices. These apps help businesses identify active RFID tags, verify tag functionality, and enhance security by preventing unauthorized tracking devices.
RFID Frequency Considerations
RFID operates at various frequencies, each suited for different applications:
1. Low Frequency (LF, 125-134 kHz)
Ideal for access control and animal tracking. LF RFID tags have a shorter read range, typically up to a few inches, making them perfect for applications that require close-proximity scanning, such as key fobs, pet microchips, and livestock tracking.
2. High Frequency (HF, 13.56 MHz)
Used for payment systems and library books. HF RFID offers moderate read ranges of up to a few feet and is widely used in contactless credit cards, smart ticketing, and secure identification systems like passports and hotel key cards. HF is preferred for applications requiring secure data transmission and anti-counterfeiting measures.
3. Ultra-High Frequency (UHF, 860-960 MHz)
Preferred for supply chain tracking and asset management. UHF RFID has a much longer read range, sometimes exceeding 30 feet, making it ideal for tracking large volumes of goods in warehouses, retail stores, and logistics networks. Due to its higher data transmission rate, UHF is the most commonly used frequency for industrial and commercial applications.
Conclusion
Radio Frequency Identification Sensor & Tracking technology is revolutionizing the way businesses manage assets and track inventory. With the integration of RFID sensors, tracking applications, and frequency-specific solutions, industries can achieve greater accuracy, efficiency, and security. As RFID technology continues to evolve, its adoption across multiple sectors will only grow, making it a vital component of modern-day automation and digital transformation.
For inquiries or further information on RFID solutions, feel free to contact us. Our team is ready to assist you with tailored guidance and expert support.